Cognos Real time Questions And Answers
What is a Fact Table?
A fact table is also a Table in the database contains Facts (Measures such as quantity sold,
revenue, account balance) and foreign keys. ( These keys will be used to connect to various
dimension tables such as Product, Time, Customer, Staff to get information like product name,
staff name, customer name etc..)
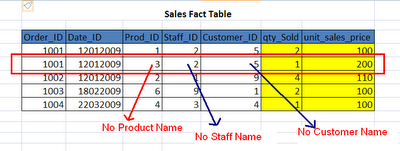
Take a look at the following Image.. The yellow shaded columns are fact columns and the
remaining columns are key columns , which will be used to connect to dimension tables..
What are Dimensional Tables..?
Dimension Tables are also tables and contains descriptive information used to describe the
rows in the fact table. look at the following fact table row....
There is no product Name, no staff name, no Customer name. With out having these names,
how do you describe the qty_sold as 1 and unit_sales_price as 200..? We can't..!
By looking prod_id (3), customer_id (5) in the product dimension and Customer dimension,
we will get product name as "Santoor" and customer name as "Jhon". So, by using dimensional
tables we can describe fact rows with information such as product name, customer name etc..
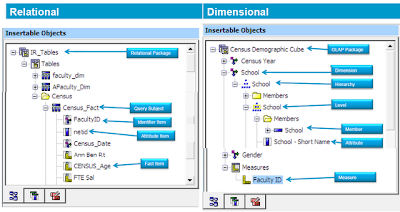
Cognos Report Studio: Prompt Expressions between Relational and Dimensional Packages..
Prompt expressions use the following syntax, where p represents the parameter name.
You can also use these expressions to create parameterized data items.
Relational: Detail Filter
|
Dimensional: slicer expression or filter expressions
|
[data item] = ?p?
for single-select prompts
|
[level or hierarchy]->?p?
For single-select member prompts and master detail relationships
|
[data item] in ?p?
for multi-select prompts
|
set([level or hierarchy]->?p?)
For multi-select member prompts
|
Difference between group by clause and order by clause
In a single sentence we can differentiate group by clause and order by clause as follows..
group by: This clause is used to group the records of a table based on their common properties and then we apply group functions such as sum(), max(), min(), count() on the groups.
order by: This clause is used to sort ( either ascending or descending ) the records based on a field or column of the table
EXPLANATION ( group by )
Group by clause is used to group the rows based on their common properties. For example, we can group the records of employee table by department, by manager, by job etc.,
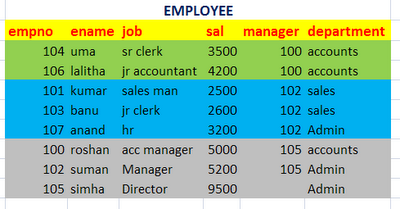
See the following table….
If we apply grouping on departments column, the records will be grouped based on departments as follows..
If we apply grouping on Manager column, the records will be arranged as follows..
Advantages of grouping:
We can apply group functions such as sum(), max(), min(), count() on groups to find total salary being drawn by each and every group, we can find maximum salary for each group, we can find number of employees have been in each and every group, etc..
For example let us try to find total salary being drawn by each and every departments..
Select department, sum(Sal) from EMPLOYEE group by department;
When we execute the above query, the execution will be done in the following steps
1) 1)The records will be grouped based on departments
2) 2)Totals will be calculated for each and every group
3) 3)One record will be returned from each group as a result
See the following transitions…
Do's and Dont's:
1) All the columns that have been written after "select" clause must appear in group by clause
Ex: select department, job, sum(sal) from employee group by department;
the above query is wrong, because the column "job" was not included after group by clause. the correct is...
select department, job, sum(sal) from employee group by department,job;
2) whatever the column we use in group function, that need not to appear in group by clause. In the above query the column "sal" has been used in sum( ) function. Here, the column "sal" is not necessary to be appeared in the group by clause.
EXPLANATION ( order by )
order by clause can only be used to sort the records based on values of a column and we cant apply any group functions. There are two types of sortings, 1) Ascending 2) Descending
Ascending: This is the default order of order by clause. This method arranges elements in A to Z(0-9) order
select * from employee order by ename;
Descending : This method arranges elements in Z to A (9 to 0) order.
select * from employee order by ename desc;
Fact less Fact Table?
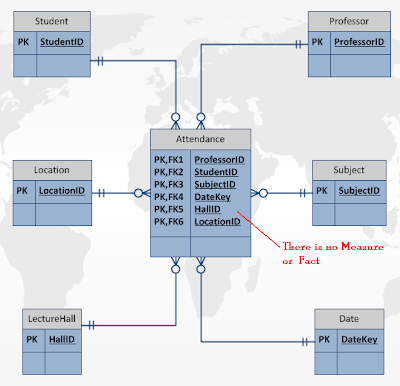
Fact less Fact table does not contain any facts. Generally Fact less fact tables are used to record the events such as students attendance, attendance of participants for an Event like a Meeting. Actually this is not a Fact table but due its position we should call it as Fact table without facts.. Look at the following image..
See the attendance Table in the Image, There is no measure or fact but Attendance Table sits like a Fact table and also have the connections to dimension tables and hence we can say that it is Fact Table and since it does not contain any measures so that we can call it as fact less fact table.
Now Let us understand the use of the Attendance Fact less Fact table....
If a student attended a class then we enter a Record in Attendance table else no row will be stored. Only aggregation here is possible only count
Making the Size of Select & Search Prompt Dynamic
By default, The width of Select & Search prompt is fixed and therefore wide text will cut off.....
Note: The following Technique is only Applicable for Cognos 8.4 Fix Pack 2 and Higher..
STEPS:
1) Locate for a File properties.js in the location ...c8\webcontent\prompting (on the machine where you installed cognos 8 gateway)
2) Take a back of it ( This backup is useful to restore the file properties.js if any thing goes wrong)3) Open the file with any Text editor and search for the line.. "SYSTEMPROPERTY_CSEARCH_AUTO_RESIZE_RESULT_LIST=FALSE"4) Replace FALSE with TRUE
5) Save the file
6) Launch the cognos and check the prompt you can see as follows.









No comments:
Post a Comment